标题中的Get和Post是请求的两种方式,同步和异步属于实现的方法,Get方式有同步和异步两种方法,Post同理也有两种。稍微有点Web知识的,对Get和Post应该不会陌生,常说的请求处理响应,基本上请求的是都是这两个哥们,Http最开始定义的与服务器交互的方式有八种,不过随着时间的进化,现在基本上使用的只剩下这两种,有兴趣的可以参考本人之前的博客,iOS客户端需要和服务端打交道,Get和Post是跑不了的,本文中包含iOS代码和少量Java服务端代码,开始正题吧.
Get和Post同步请求
Get和Post同步请求的时候最常见的是登录,输入各种密码才能看到的功能,必须是同步,异步在Web上局部刷新的时候用的比较多,比较耗时的时候执行异步请求,可以让客户先看到一部分功能,然后慢慢刷新,举个例子就是餐馆吃饭的时候点了十几个菜,给你先上一两个吃着,之后给别人上,剩下的慢慢上。大概就是这样的。弄了几个按钮先上图:

先贴下同步请求的代码:
//设置URL路径 NSString *urlStr=[NSString stringWithFormat:@"http://localhost:8080/MyWeb/Book?username=%@&password=%@&type=get",@"博客园",@"keso"]; urlStr=[urlStr stringByAddingPercentEscapesUsingEncoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding]; NSURL *url=[NSURL URLWithString:urlStr]; //通过URL设置网络请求 NSURLRequest *request = [[NSURLRequest alloc]initWithURL:url cachePolicy:NSURLRequestUseProtocolCachePolicy timeoutInterval:10]; NSError *error=nil; //获取服务器数据 NSData *requestData= [NSURLConnection sendSynchronousRequest:request returningResponse:nil error:&error]; if (error) { NSLog(@"错误信息:%@",[error localizedDescription]); }else{ NSString *result=[[NSString alloc]initWithData:requestData encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding]; NSLog(@"返回结果:%@",result); } 代码很多,需要解释一下:
①URL如果有中文无法传递,需要编码一下:
[urlStr stringByAddingPercentEscapesUsingEncoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding];
②设置网路请求中的代码,有两个参数,最后一个设置请求的时间,这个不用说什么,重点说下缓存策略cachePolicy,系统中的定义如下:
typedef NS_ENUM(NSUInteger, NSURLRequestCachePolicy){ NSURLRequestUseProtocolCachePolicy = 0, NSURLRequestReloadIgnoringLocalCacheData = 1, NSURLRequestReloadIgnoringLocalAndRemoteCacheData = 4, // Unimplemented NSURLRequestReloadIgnoringCacheData = NSURLRequestReloadIgnoringLocalCacheData, NSURLRequestReturnCacheDataElseLoad = 2, NSURLRequestReturnCacheDataDontLoad = 3, NSURLRequestReloadRevalidatingCacheData = 5, // Unimplemented}; NSURLRequestUseProtocolCachePolicy(基础策略),NSURLRequestReloadIgnoringLocalCacheData(忽略本地缓存);
NSURLRequestReloadIgnoringLocalAndRemoteCacheData(无视任何缓存策略,无论是本地的还是远程的,总是从原地址重新下载);
NSURLRequestReturnCacheDataElseLoad(首先使用缓存,如果没有本地缓存,才从原地址下载);
NSURLRequestReturnCacheDataDontLoad(使用本地缓存,从不下载,如果本地没有缓存,则请求失败,此策略多用于离线操作);
NSURLRequestReloadRevalidatingCacheData(如果本地缓存是有效的则不下载,其他任何情况都从原地址重新下载);
Java服务端代码:
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8;"); PrintWriter out = response.getWriter(); System.out.println(request.getParameter("username")); System.out.println(request.getParameter("password")); if (request.getParameter("type") == null) { out.print("默认测试"); } else { if (request.getParameter("type").equals("async")) { out.print("异步Get请求"); } else { out.print("Get请求"); } } } 最终效果如下:
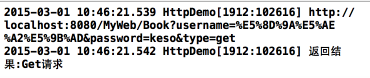
Post请求的代码,基本跟Get类型,有注释,就不多解释了:
//设置URL NSURL *url=[NSURL URLWithString:@"http://localhost:8080/MyWeb/Book"]; //创建请求 NSMutableURLRequest *request = [[NSMutableURLRequest alloc]initWithURL:url cachePolicy:NSURLRequestUseProtocolCachePolicy timeoutInterval:10]; [request setHTTPMethod:@"POST"];//设置请求方式为POST,默认为GET NSString *param= @"Name=博客园&Address=http://www.cnblogs.com/xiaofeixiang&Type=post";//设置参数 NSData *data = [param dataUsingEncoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding]; [request setHTTPBody:data]; //连接服务器 NSData *received = [NSURLConnection sendSynchronousRequest:request returningResponse:nil error:nil]; NSString *result= [[NSString alloc]initWithData:received encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding]; NSLog(@"%@",result);
Java服务端代码:
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8"); response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8"); PrintWriter out = response.getWriter(); System.out.println("姓名:" + request.getParameter("Name")); System.out.println("地址:" + request.getParameter("Address")); System.out.println("类型:" + request.getParameter("Type")); if (request.getParameter("Type").equals("async")) { out.print("异步请求"); } else { out.print("Post请求"); } } 效果如下:
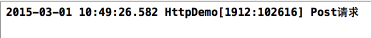
Get和Post异步请求
异步实现的时候需要实现协议NSURLConnectionDataDelegate,Get异步代码如下:
//设置URL路径 NSString *urlStr=[NSString stringWithFormat:@"http://localhost:8080/MyWeb/Book?username=%@&password=%s&type=async",@"FlyElephant","keso"]; urlStr=[urlStr stringByAddingPercentEscapesUsingEncoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding]; NSURL *url=[NSURL URLWithString:urlStr]; //创建请求 NSURLRequest *request = [[NSURLRequest alloc]initWithURL:url cachePolicy:NSURLRequestUseProtocolCachePolicy timeoutInterval:10]; //连接服务器 NSURLConnection *connection = [[NSURLConnection alloc]initWithRequest:request delegate:self];
实现协议的连接过程的方法:
-(void)connection:(NSURLConnection *)connection didReceiveResponse:(NSURLResponse *)response{ NSHTTPURLResponse *res = (NSHTTPURLResponse *)response; NSLog(@"%@",[res allHeaderFields]); self.myResult = [NSMutableData data];}接收到服务器传输数据的时候调用,此方法根据数据大小执行若干次-(void)connection:(NSURLConnection *)connection didReceiveData:(NSData *)data{ [self.myResult appendData:data]; }//数据传输完成之后执行方法-(void)connectionDidFinishLoading:(NSURLConnection *)connection{ NSString *receiveStr = [[NSString alloc]initWithData:self.myResult encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding]; NSLog(@"%@",receiveStr); }//网络请求时出现错误(断网,连接超时)执行方法-(void)connection:(NSURLConnection *)connection didFailWithError:(NSError *)error{ NSLog(@"%@",[error localizedDescription]);} 异步传输的过程数据需要拼接,所以这个时候需要设置一个属性接收数据:
@property (strong,nonatomic) NSMutableData *myResult;
效果如下:
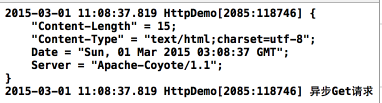
Post异步传递代码:
//设置URL NSURL *url=[NSURL URLWithString:@"http://localhost:8080/MyWeb/Book"]; //设置请求 NSMutableURLRequest *request = [[NSMutableURLRequest alloc]initWithURL:url cachePolicy:NSURLRequestUseProtocolCachePolicy timeoutInterval:10]; [request setHTTPMethod:@"POST"];//设置请求方式为POST,默认为GET NSString *param= @"Name=keso&Address=http://www.cnblogs.com/xiaofeixiang&Type=async";//设置参数 NSData *data = [param dataUsingEncoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding]; [request setHTTPBody:data]; //连接服务器 NSURLConnection *connection = [[NSURLConnection alloc]initWithRequest:request delegate:self];
效果如下:
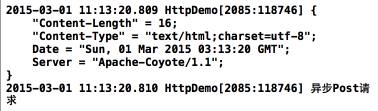
异步的请求比较简单,需要的方法都已经被封装好了,需要注意数据是动态拼接的,请求的代码都是在Java Servlet中实现的,Java项目中的目录如下:
Book.java中代码如下:
import java.io.IOException;import java.io.PrintWriter;import java.net.URLDecoder;import java.net.URLEncoder;import javax.servlet.ServletException;import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;/** * Servlet implementation class Book */@WebServlet("/Book")public class Book extends HttpServlet { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; /** * @see HttpServlet#HttpServlet() */ public Book() { super(); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } /** * @see HttpServlet#doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse * response) */ protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8;"); PrintWriter out = response.getWriter(); System.out.println(request.getParameter("username")); System.out.println(request.getParameter("password")); if (request.getParameter("type") == null) { out.print("默认测试"); } else { if (request.getParameter("type").equals("async")) { out.print("异步Get请求"); } else { out.print("Get请求"); } } } /** * @see HttpServlet#doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse * response) */ protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8"); response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8"); PrintWriter out = response.getWriter(); System.out.println("姓名:" + request.getParameter("Name")); System.out.println("地址:" + request.getParameter("Address")); System.out.println("类型:" + request.getParameter("Type")); if (request.getParameter("Type").equals("async")) { out.print("异步Post请求"); } else { out.print("Post请求"); } }} Get和Post总结
①同步请求一旦发送,程序将停止用户交互,直至服务器返回数据完成,才可以进行下一步操作(例如登录验证);
②异步请求不会阻塞主线程,会建立一个新的线程来操作,发出异步请求后,依然可以对UI进行操作,程序可以继续运行;
③Get请求,将参数直接写在访问路径上,容易被外界看到,安全性不高,地址最多255字节;
④Post请求,将参数放到body里面,安全性高,不易被捕获;